The liver is a remarkable organ that performs vital functions essential for overall health. From detoxification to metabolism and nutrient storage, it works tirelessly to keep your body in balance. This blog explores how diet and lifestyle choices, especially the best foods for liver health—impact liver function and offers actionable tips for long-term care.
Key Functions of the Liver
- Bile Production: Helps digest fats in the stomach.
- Cholesterol and Protein Synthesis: Produces proteins and cholesterol for fat transport.
- Blood Detoxification: Removes harmful substances, including drugs and toxins.
- Blood Clotting: Produces proteins that aid in clotting when injuries occur.
- Immune Support: Fights infections by removing bacteria and producing immune factors.
The Role of Diet in Liver Health
Your liver’s health is intricately linked to your diet. What you eat can either support its functions or lead to complications such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or other liver disorders.
Key Dietary Considerations for Liver Health
- Weight Management
Obesity is a major risk factor for liver disorders. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity significantly improves liver function and reduces the risk of NAFLD. - Control Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
Excess sugar and refined carbs lead to fat accumulation in the liver. Reducing sugary drinks, sweets, and processed foods can alleviate stress on the liver. - Adopt a Balanced Diet
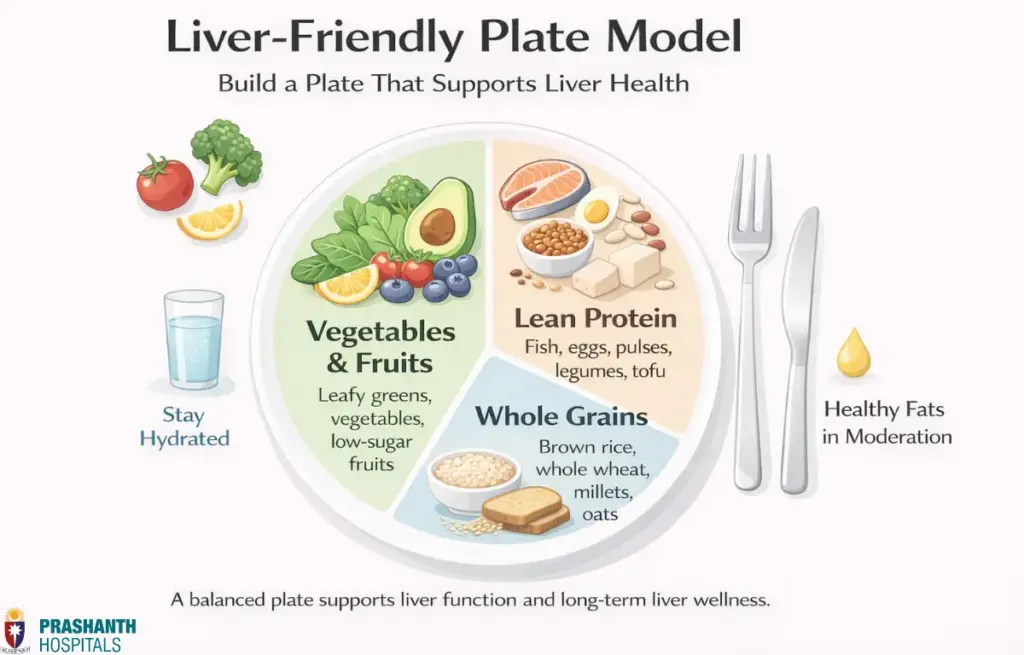
Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Proper hydration is essential for flushing toxins from the liver. Including the best foods for liver health in your meals ensures your liver gets the nutrients it needs to function efficiently.
Top Liver-Friendly Foods
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Rich in antioxidants and fiber for detoxification.
- Berries, cruciferous vegetables, spinach, and carrots. These are some of the best foods for liver health.
- Whole Grains
- Promote steady energy levels and digestive health.
- Examples: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread.
- Lean Proteins
- Essential for liver repair and overall function.
- Include: Chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats
- Beneficial for reducing inflammation.
- Found in: Avocados, nuts, olive oil, and seeds.
- Fatty Fish
- High in omega-3 fatty acids, which support liver function.
- Best picks: Salmon, mackerel, and trout.
- Herbs and Spices
- Anti-inflammatory properties help detoxify the liver.
- Examples: Turmeric, ginger, and garlic.
- Nuts
- Rich in vitamin E, healthy fats, and antioxidants.
- Best options: Walnuts and almonds.
- Cruciferous Vegetables
- Boost liver detox processes.
- Include: Broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts.
- Beets
- Contain betaine, which aids in reducing fatty liver risk.
- Grapefruit
- Packed with antioxidants and vitamin C for detoxification.
Including foods good for liver health like grapefruit regularly can support liver function.
Lifestyle Tips for Liver Health
- Exercise Regularly
- Physical activity helps burn triglycerides and reduce liver fat.
- Avoid Toxins
- Minimize exposure to harmful chemicals and smoking.
- Limit Alcohol
- Excessive drinking damages liver cells and increases fat buildup.
- Practice Safe Hygiene
- Wash hands regularly and avoid sharing personal items.
- Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water to help the liver flush out toxins.
- Follow Medication Instructions
- Avoid mixing alcohol with medications and follow your doctor’s advice.
Foods to Avoid
- Processed Foods: High in sugar, trans fats, and refined carbs. These are some of the key foods to avoid for liver health.
- Alcohol: Excessive consumption damages liver cells.
- High-Fructose Corn Syrup: Increases fat buildup in the liver.
Weight Loss for Liver Disease
Even a small reduction in weight can make a big difference for liver health. Losing just 5% of your body weight can reduce fat buildup in the liver. A 7–10% weight loss can improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and support reversal of fatty liver changes over time.
Nutrition Tips for Weight Loss and Liver Health
Fill Half Your Plate with Vegetables and Fruits: Aim for colorful, non-starchy vegetables and fruits. They provide fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins that support liver function and keep you feeling full.
Include Healthy Liver-Friendly Fats: Incorporate foods good for liver health such as nuts, seeds, fatty fish, olive oil, and avocado. These fats nourish your liver but watch portion sizes to avoid excess calories.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Reduce intake of red meat, butter, cheese, and packaged foods with trans fats. Keeping these minimal helps reduce liver stress and supports fat loss.
Move Daily: Even 5–10 minutes of light exercise, like walking or stretching, can improve liver function. Gradually increase activity to 150 minutes per week, including brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, to support weight loss and overall health.
Stay Accountable: Engage family or friends in your journey. Sharing meals, planning walks, or joining a fitness group can make lifestyle changes easier to maintain long-term.
Focus on the Best Foods for Liver Health: Whole grains, leafy greens, legumes, and berries are excellent choices that complement weight loss efforts and improve liver function naturally.
A Healthier Liver for a Healthier Life
Your liver works tirelessly to keep your body functioning at its best. To support this vital organ, focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and mindful lifestyle choices. Incorporating the best foods for liver health and avoiding harmful substances will not only enhance liver function but also improve your overall well-being.
Start small by adding antioxidant-rich foods to your meals and staying hydrated. Over time, these gradual changes can make a big difference. If you’re wondering which food is good for liver health, start with leafy greens, berries, and fatty fish. Remember, a healthy liver equals a healthier life!